1、[LG] Adaptive Computation with Elastic Input Sequence
2、[LG] Efficient Graph Field Integrators Meet Point Clouds
3、[LG] Massively Scaling Heteroscedastic Classifiers
4、[LG] Supervision Complexity and its Role in Knowledge Distillation
5、[LG] EmbedDistill: A Geometric Knowledge Distillation for Information Retrieval
[CV] Deep Learning for Human Parsing: A Survey
[AS]《AudioLDM: Text-to-Audio Generation with Latent Diffusion Models》H Liu, Z Chen, Y Yuan, X Mei, X Liu, D Mandic, W Wang, M D. Plumbley
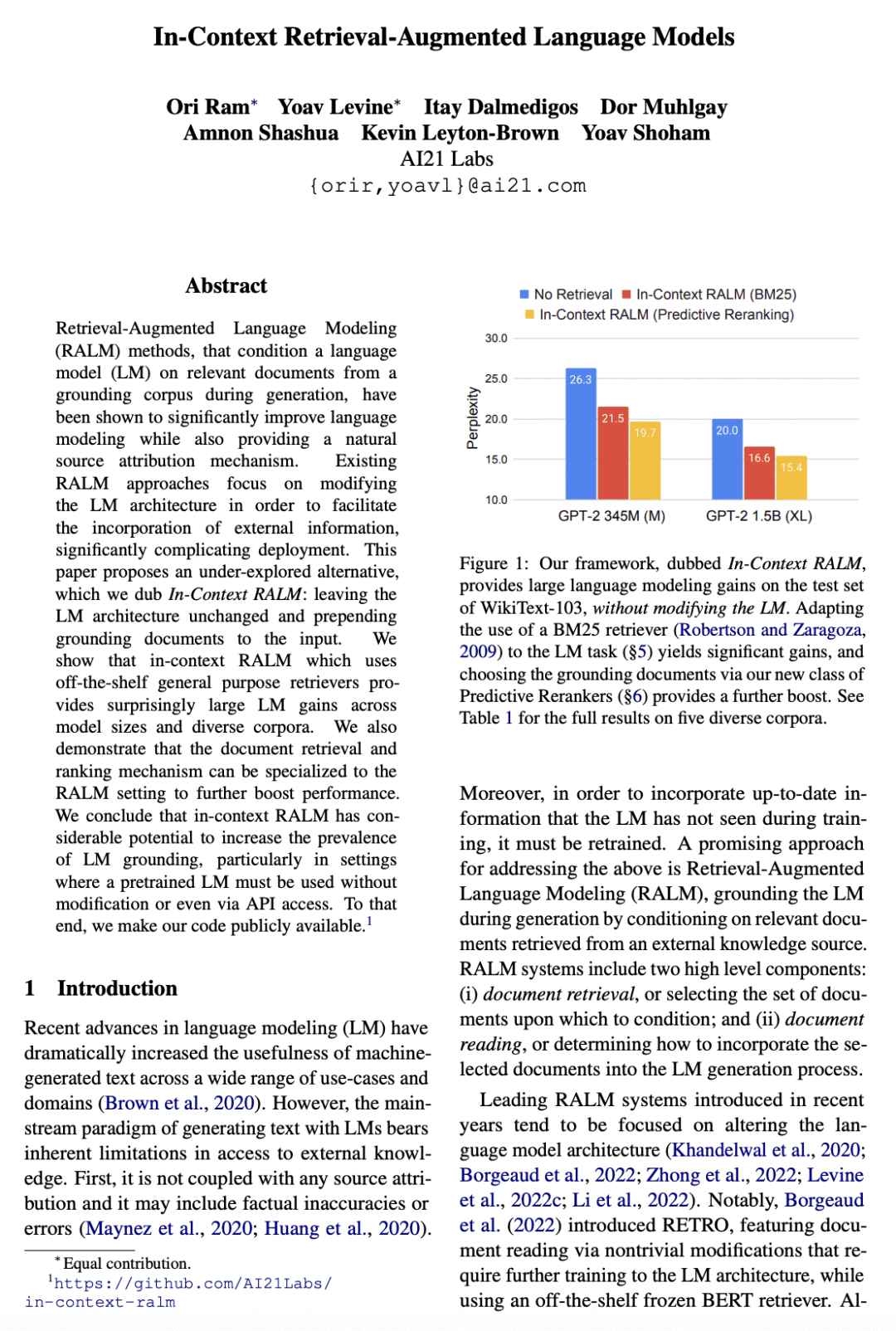
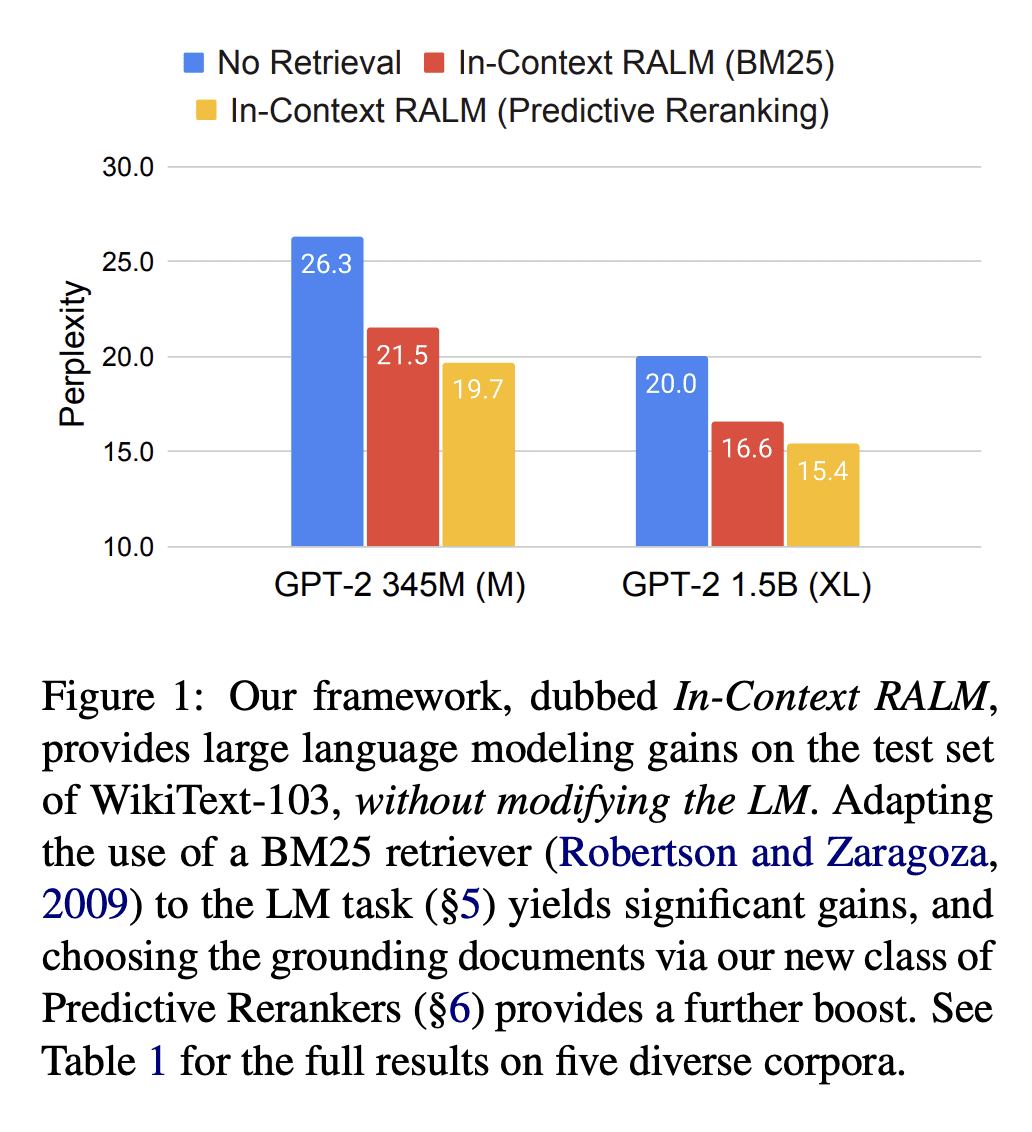
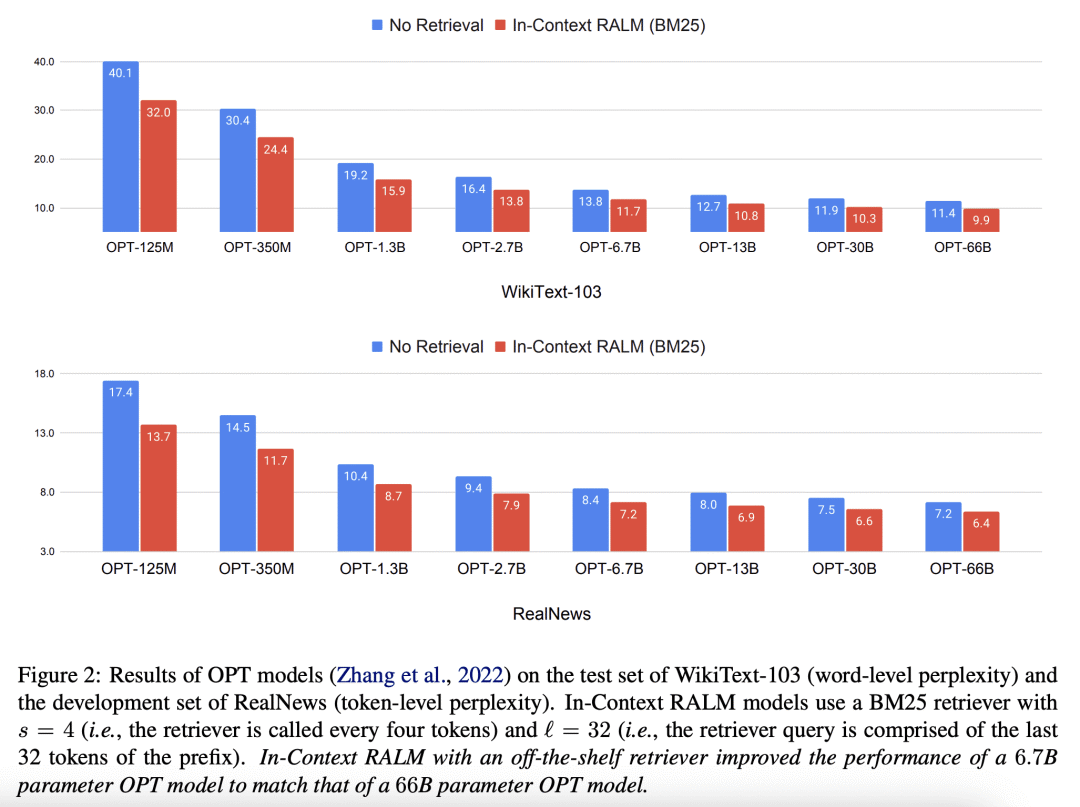
[CL] In-Context Retrieval-Augmented Language Models
[LG] FLAME: A small language model for spreadsheet formulas
摘要:弹性输入序列的自适应计算、点云与高效图场积分器、大规模尺度异方差分类器、监督复杂性及其在知识蒸馏中的作用、面向信息检索的几何知识蒸馏、深度学习人体解析综述、基于潜扩散模型的文本到音频生成、上下文检索增强语言模型、面向电子表格公式的小型语言模型
1、[LG] Adaptive Computation with Elastic Input Sequence
F Xue, V Likhosherstov, A Arnab, N Houlsby, M Dehghani, Y You
[Google Brain]
弹性输入序列的自适应计算
要点:
-
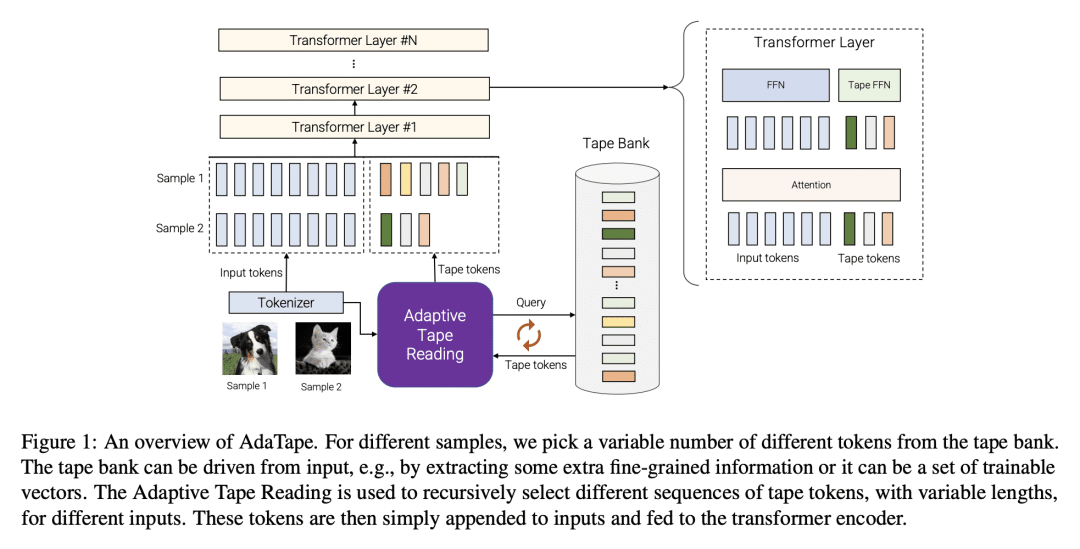
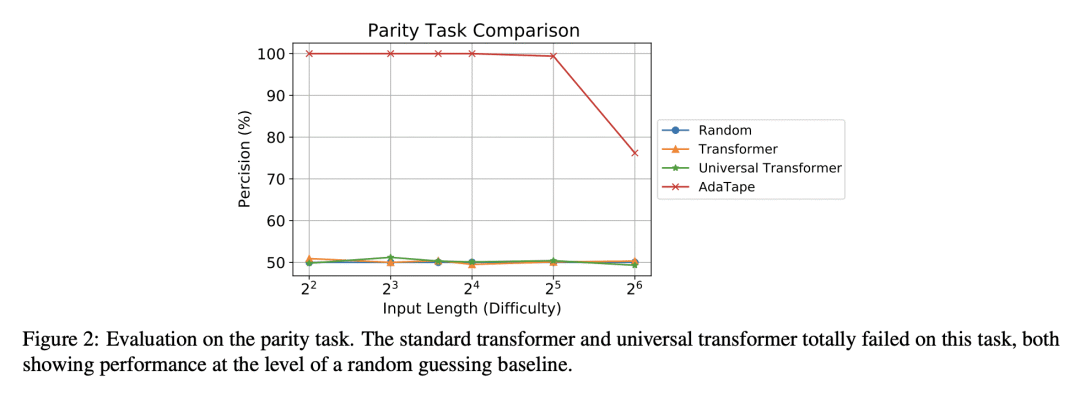
提出 AdaTape,一种在神经网络中实现自适应计算的新策略; -
用动态 tape token 实现动态计算和输入序列适应; -
提出自适应 Tape 读取(ATR)算法,以生成动态序列内容和长度; -
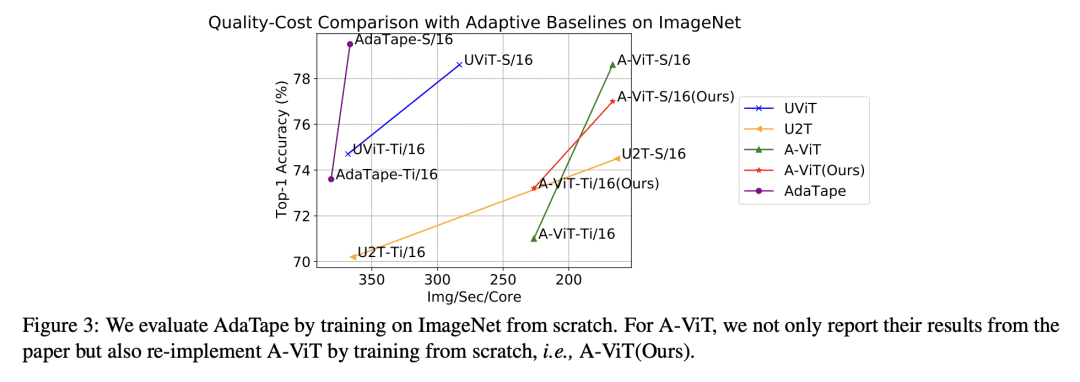
与标准 Transformer 和现有的自适应架构 Transformer 相比,在图像识别任务上的性能有所提高,有可能解决具有挑战性的任务。
一句话总结:
AdaTape 是神经网络一种新的自适应计算方法,用动态 tape token 和自适应 Tape 读取算法来生成输入序列,可提高图像识别任务的性能。
摘要:
在解决一个问题时,人在使用的信息类型、采取的流程以及接近和解决该问题所花费的时间方面具有自适应能力。然而,大多数标准的神经网络在不同的样本上具有相同的函数类型和固定的计算预算,而不论其性质和难度如何。自适应性是一个强大的范式,因为它不仅赋予了从业者与这些模型的下游使用有关的灵活性,而且还可以作为解决某些具有挑战性的问题类别的一个强大的归纳偏差。本文提出一种新策略——AdaTape,通过自适应 tape token 在神经网络中实现动态计算。通过给现有的架构配备动态读写 tape,AdaTape 可采用弹性输入序列。用从 tape bank 中获得的 tape token 自适应生成输入序列,这些 tape token 可以是可训练的,也可以从输入数据中生成。本文分析了获得动态序列内容和长度的挑战和要求,并提出了自适应 Tape 阅读器(ATR)算法来实现这两个目标。通过对图像识别任务的广泛实验,表明 AdaTape 可以在保持计算成本的情况下取得更好的性能。
When solving a problem, human beings have the adaptive ability in terms of the type of information they use, the procedure they take, and the amount of time they spend approaching and solving the problem. However, most standard neural networks have the same function type and fixed computation budget on different samples regardless of their nature and difficulty. Adaptivity is a powerful paradigm as it not only imbues practitioners with flexibility pertaining to the downstream usage of these models but can also serve as a powerful inductive bias for solving certain challenging classes of problems. In this work, we propose a new strategy, AdaTape, that enables dynamic computation in neural networks via adaptive tape tokens. AdaTape employs an elastic input sequence by equipping an existing architecture with a dynamic read-and-write tape. Specifically, we adaptively generate input sequences using tape tokens obtained from a tape bank that can either be trainable or generated from input data. We analyze the challenges and requirements to obtain dynamic sequence content and length, and propose the Adaptive Tape Reader (ATR) algorithm to achieve both objectives. Via extensive experiments on image recognition tasks, we show that AdaTape can achieve better performance while maintaining the computational cost.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.13195

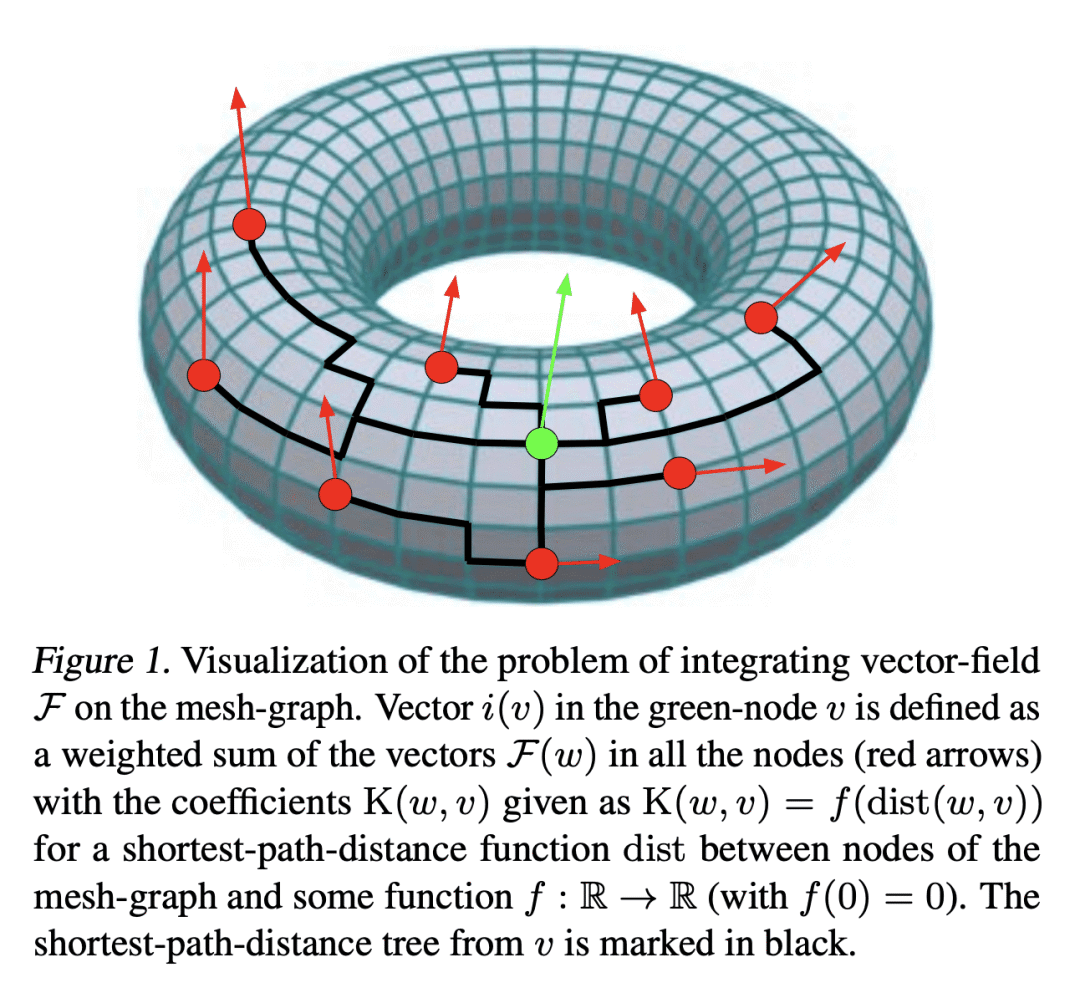
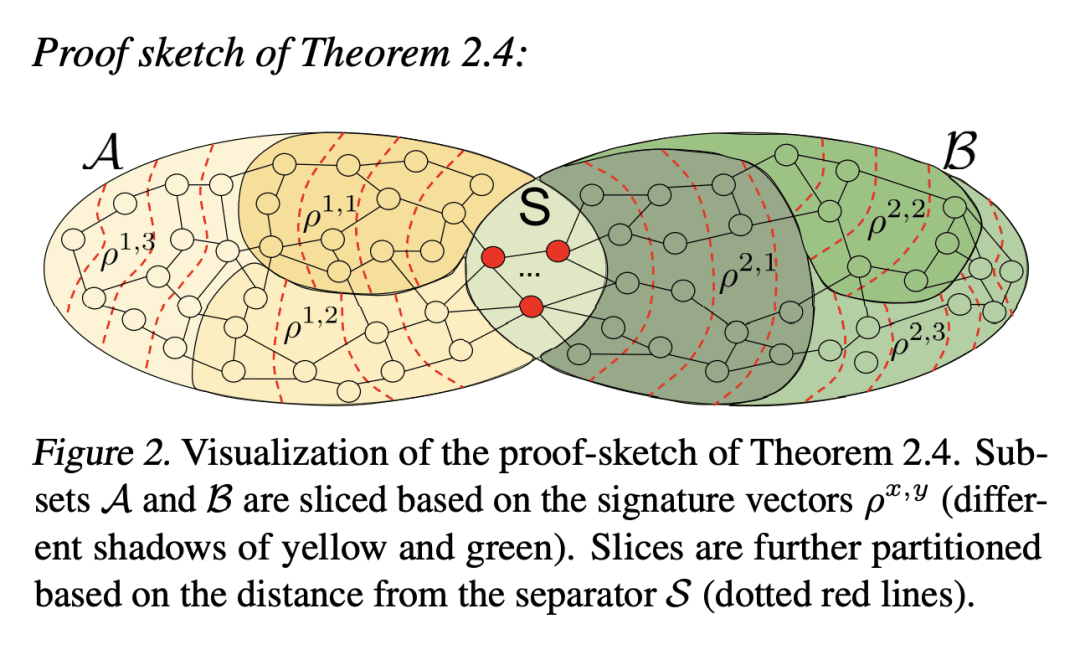
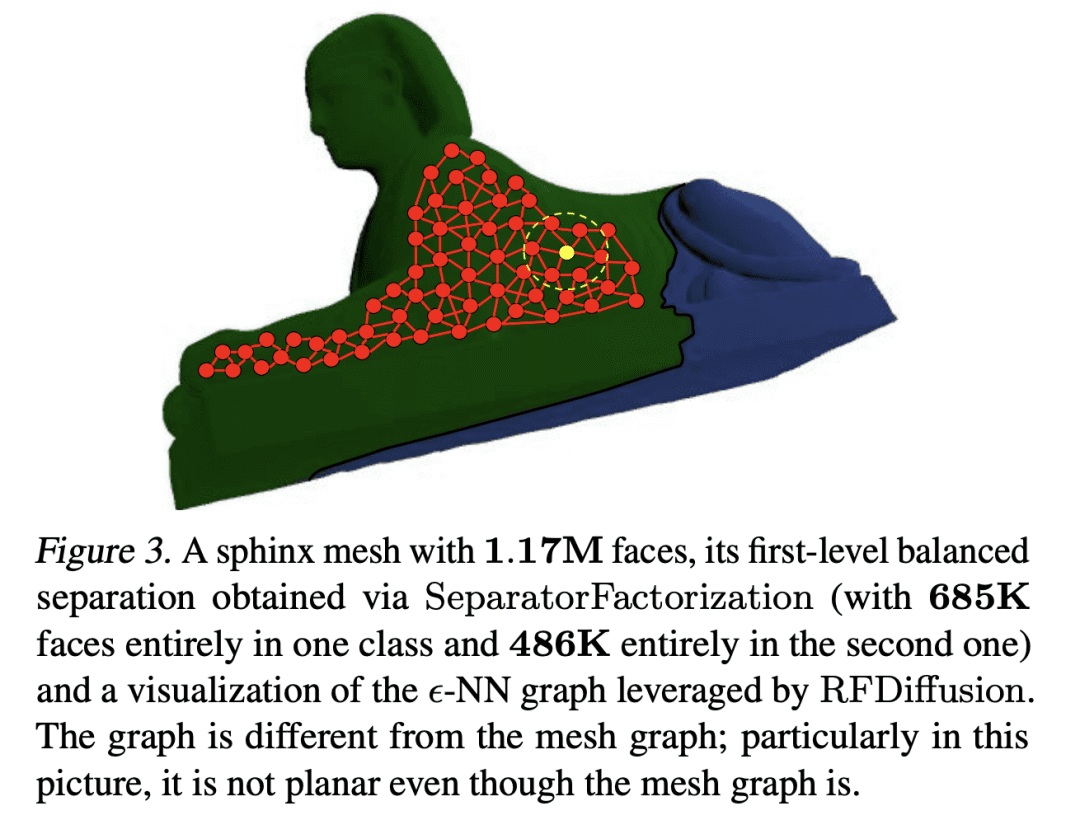
2、[LG] Efficient Graph Field Integrators Meet Point Clouds
K Choromanski, A Sehanobish, H Lin, Y Zhao, E Berger…
[Google Research & Columbia University & Haifa University & Stanford University & …]
点云与高效图场积分器
要点:
-
提出两类新算法,SeparatorFactorization (SF) 和 RFDiffusion (RFD),用于在编码点云的图上进行有效的场积分; -
SF利用了点云网图的有界属性,对近似的图场积分具有 O(N log2(N)) 的时间复杂度,在某些特殊情况下有额外的计算收益; -
RFD 使用 epsilon-nearest-neighbor 图表示,对近似图场积分来说,具有 O(N) 的时间复杂度,利用了基于随机特征嵌入。
一句话总结:
提出两种在编码点云的图上进行高效场积分的算法,利用网图的有界性及epsilon-nearest-neighbor图表示,并对其有效性进行了广泛的理论分析和经验评估。
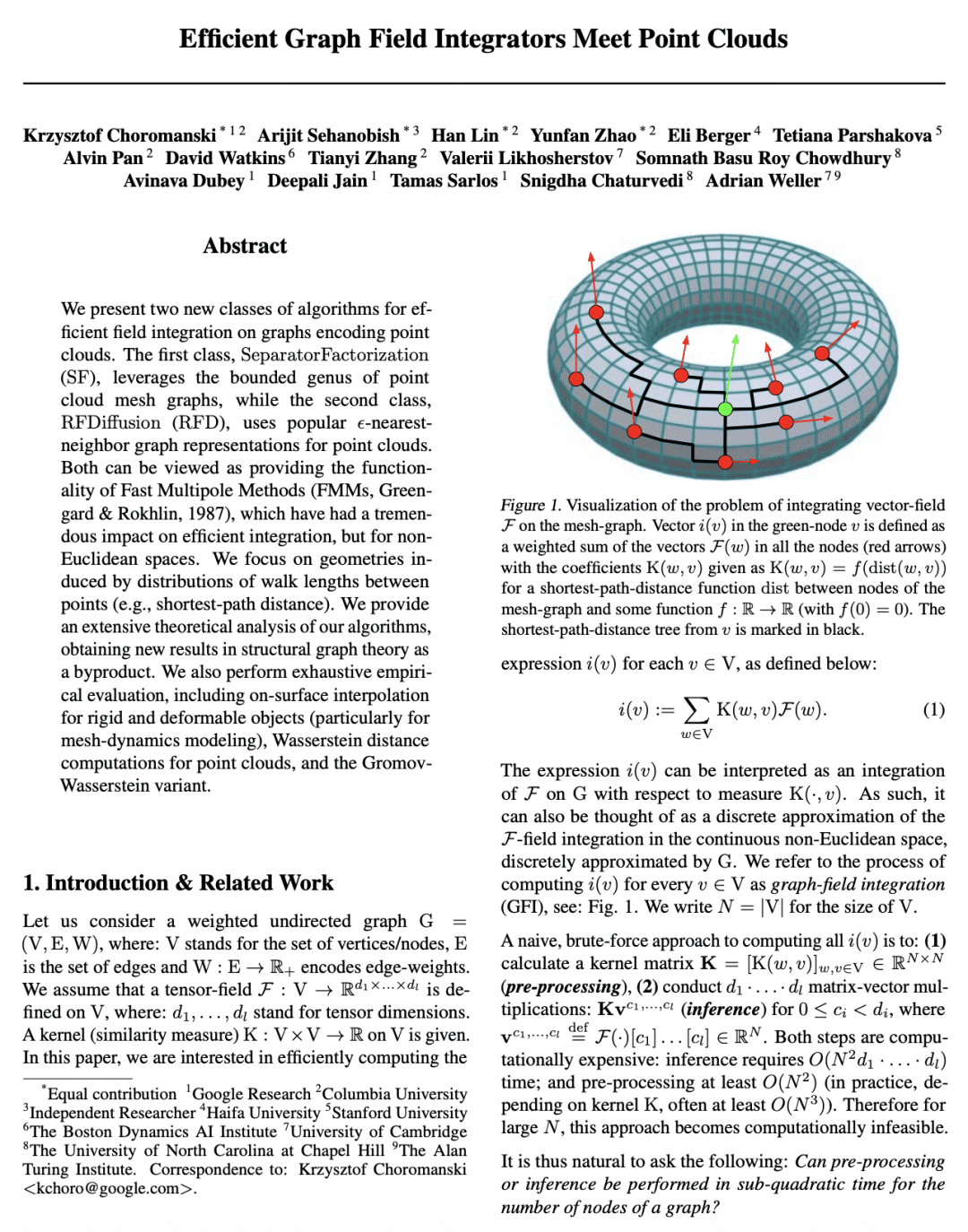
摘要:
本文提出两类新的算法,用于在编码点云的图上进行有效的场积分。第一类,SeparatorFactorization(SF),利用点云网图的有界属性,第二类,RFDiffusion(RFD),用流行的 epsilon-nearest-neighbor 图来表示点云。两者都可以看作是提供了快速多极方法(FMM)的功能,这些方法对高效积分产生了巨大的影响,但是是对于非欧几里得空间而言。本文专注于由点与点之间的漫游长度分布(例如,最短路径距离)所引起的几何形状。对所提出的算法进行了广泛的理论分析,作为副产品获得了结构图论的新结果。本文还进行了详尽的经验评估,包括刚性和可变形物体的表面插值(特别是用于网格动力学建模),点云的 Wasserstein 距离计算,以及 Gromov-Wasserstein 变体。
We present two new classes of algorithms for efficient field integration on graphs encoding point clouds. The first class, SeparatorFactorization(SF), leverages the bounded genus of point cloud mesh graphs, while the second class, RFDiffusion(RFD), uses popular epsilon-nearest-neighbor graph representations for point clouds. Both can be viewed as providing the functionality of Fast Multipole Methods (FMMs), which have had a tremendous impact on efficient integration, but for non-Euclidean spaces. We focus on geometries induced by distributions of walk lengths between points (e.g., shortest-path distance). We provide an extensive theoretical analysis of our algorithms, obtaining new results in structural graph theory as a byproduct. We also perform exhaustive empirical evaluation, including on-surface interpolation for rigid and deformable objects (particularly for mesh-dynamics modeling), Wasserstein distance computations for point clouds, and the Gromov-Wasserstein variant.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.00942
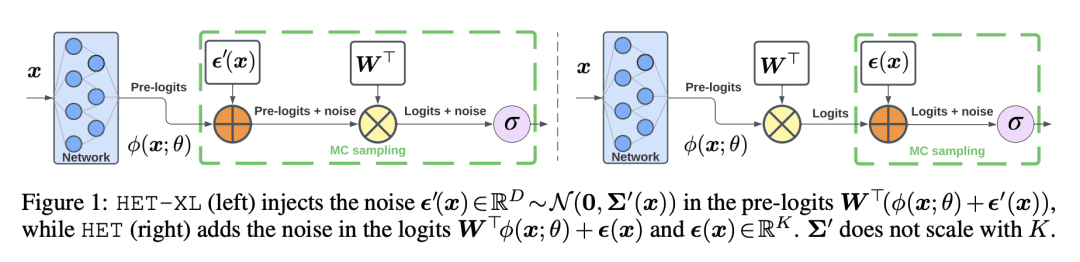
3、[LG] Massively Scaling Heteroscedastic Classifiers
M Collier, R Jenatton, B Mustafa, N Houlsby, J Berent, E Kokiopoulou
[Google AI]
大规模尺度异方差分类器
要点:
-
提出 HET-XL,一种异方差分类器,参数数量减少,在大规模问题上不需要温度超参数调整; -
HET 和 HET-H 在三个基准图像分类中表现一致; -
将 HET-XL 扩展到对比学习,提高了ImageNet 零样本分类的准确性。
一句话总结:
HET-XL 是一种异方差分类器,大大降低了部署成本,需要更少的参数,也不需要调整温度超参数。
摘要:
异方差分类器,在预测对数上学习多变量高斯分布,已被证明在有数百到数千个类的图像分类问题上表现良好。然而,与标准分类器相比,它们引入了额外的参数,这些参数与类的数量成线性比例。这使得它们不可能应用于更大规模的问题。此外,异方差分类器还引入了一个临界温度超参数,必须对其进行调整。本文提出 HET-XL,一种异方差分类器,与标准分类器相比,其参数数量与分类数无关。在所述大规模设置中,可以通过直接在训练数据上学习温度超参数来消除调整温度超参数的需要。在大型图像分类数据集上,所提方法需要的额外参数少了14倍,不需要在保持的数据集上调整温度,而且性能始终比基线异方差分类器好。HET-XL 在多模态对比学习设置中改善了 ImageNet 的零样本分类,该设置可被视为一个35亿类的分类问题。
Heteroscedastic classifiers, which learn a multivariate Gaussian distribution over prediction logits, have been shown to perform well on image classification problems with hundreds to thousands of classes. However, compared to standard classifiers, they introduce extra parameters that scale linearly with the number of classes. This makes them infeasible to apply to larger-scale problems. In addition heteroscedastic classifiers introduce a critical temperature hyperparameter which must be tuned. We propose HET-XL, a heteroscedastic classifier whose parameter count when compared to a standard classifier scales independently of the number of classes. In our large-scale settings, we show that we can remove the need to tune the temperature hyperparameter, by directly learning it on the training data. On large image classification datasets with up to 4B images and 30k classes our method requires 14X fewer additional parameters, does not require tuning the temperature on a held-out set and performs consistently better than the baseline heteroscedastic classifier. HET-XL improves ImageNet 0-shot classification in a multimodal contrastive learning setup which can be viewed as a 3.5 billion class classification problem.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.12860

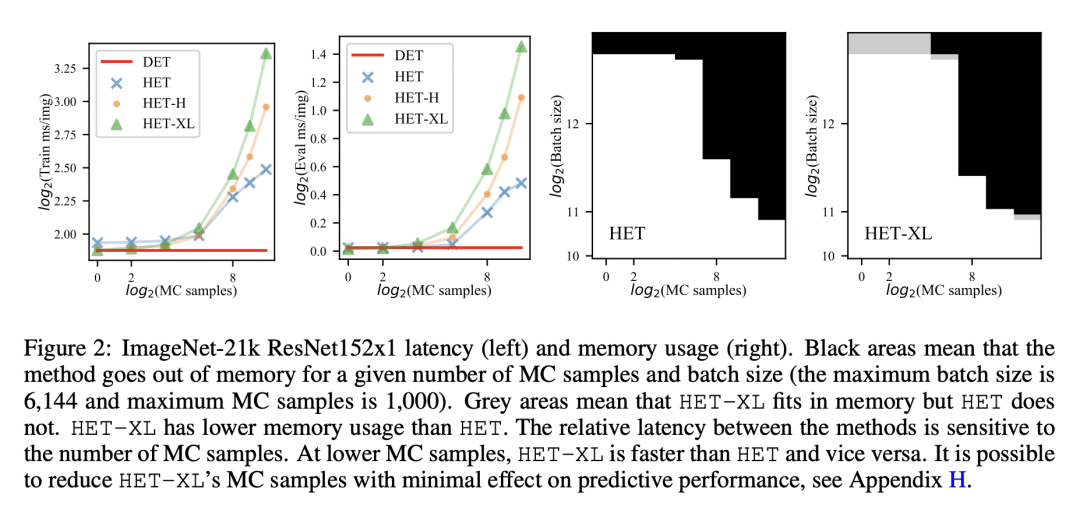
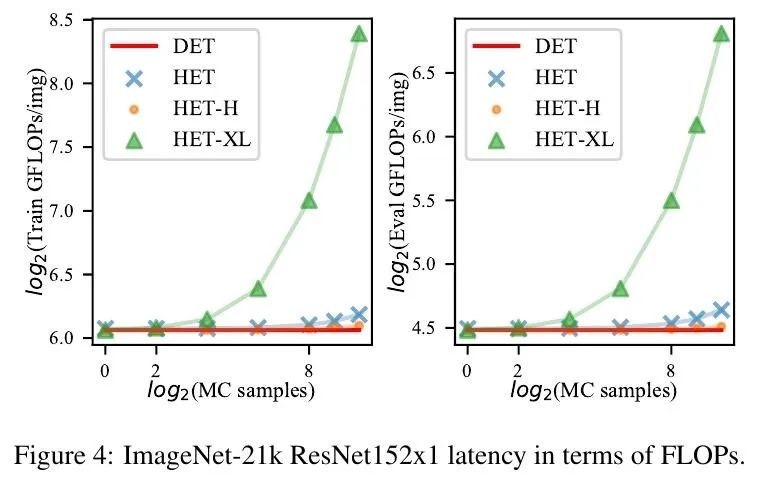
4、[LG] Supervision Complexity and its Role in Knowledge Distillation
H Harutyunyan, A S Rawat, A K Menon, S Kim, S Kumar
[Google Research NYC& USC]
监督复杂性及其在知识蒸馏中的作用
要点:
-
提出一种新的知识蒸馏的理论框架,利用监督复杂性,一种衡量教师和学生预测之间一致性的标准; -
强调了在控制学生的泛化性方面,教师的准确性、学生预测的边缘和监督复杂性之间的相互作用; -
在线蒸馏被证明是增加教师复杂性而不降低学生边缘的有效方法。
一句话总结:
提出一个新的理论框架,利用监督复杂性来理解为什么知识蒸馏能有效改善学生模型的泛化行为。
摘要:
尽管知识蒸馏很受欢迎,也很有效,但人们对它为什么有作用的理解却很有限。为了研究蒸馏得到学生的泛化行为,本文提出一种新的理论框架,利用监督复杂性:衡量教师提供的监督和学生的神经切线核之间的一致性。该框架强调了教师的准确性、学生相对于教师预测的边缘以及教师预测的复杂性之间的微妙相互作用。为蒸馏背景下普遍存在的各种技术的效用提供了严格的论证,如提前停止和温度缩放等。本文分析进一步建议使用在线蒸馏法,即学生在训练的不同阶段接受教师越来越复杂的监督。本文证明了在线蒸馏的功效,并在一系列的图像分类基准和模型架构上验证了理论结论。
Despite the popularity and efficacy of knowledge distillation, there is limited understanding of why it helps. In order to study the generalization behavior of a distilled student, we propose a new theoretical framework that leverages supervision complexity: a measure of alignment between teacher-provided supervision and the student’s neural tangent kernel. The framework highlights a delicate interplay among the teacher’s accuracy, the student’s margin with respect to the teacher predictions, and the complexity of the teacher predictions. Specifically, it provides a rigorous justification for the utility of various techniques that are prevalent in the context of distillation, such as early stopping and temperature scaling. Our analysis further suggests the use of online distillation, where a student receives increasingly more complex supervision from teachers in different stages of their training. We demonstrate efficacy of online distillation and validate the theoretical findings on a range of image classification benchmarks and model architectures.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.12245

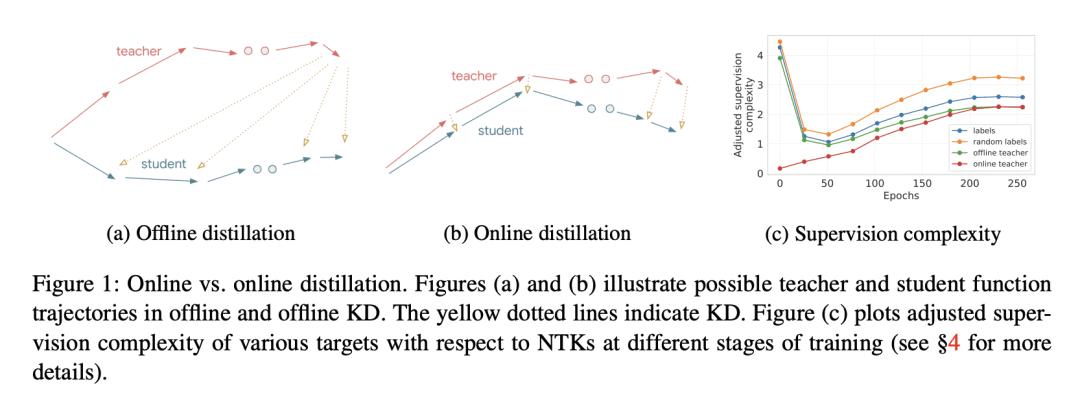
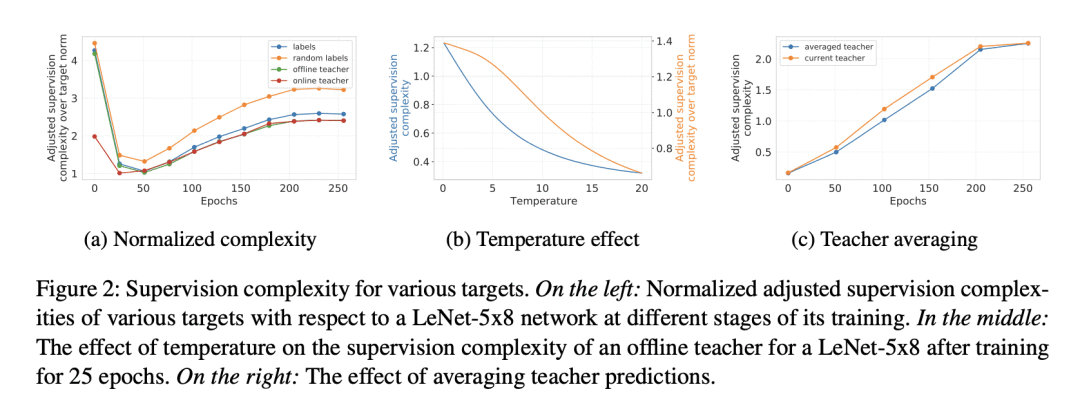
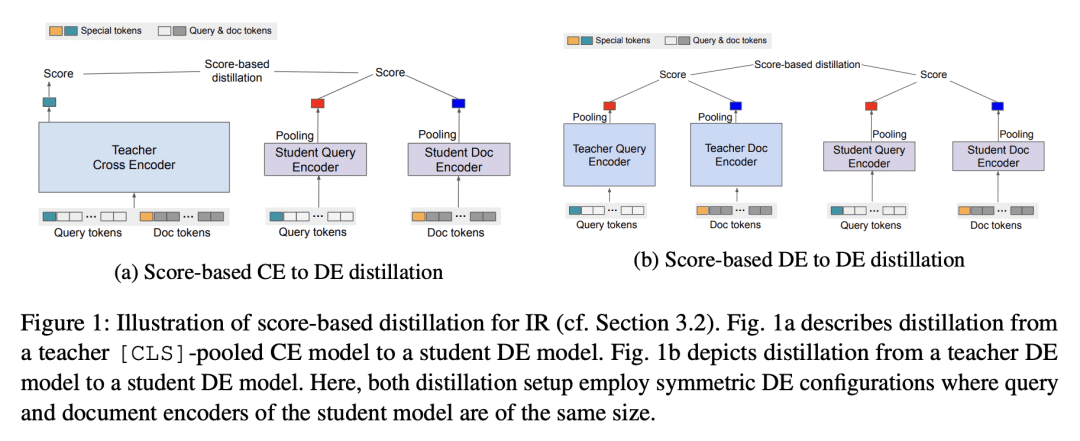
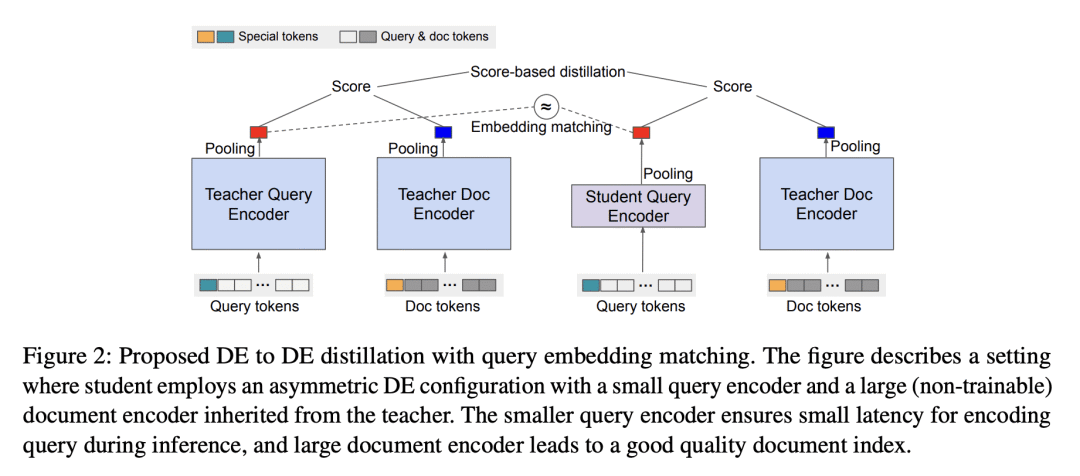
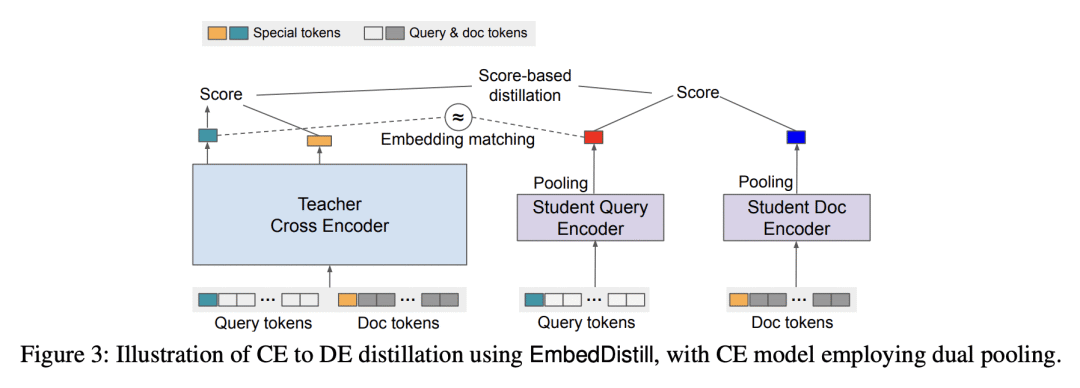
5、[LG] EmbedDistill: A Geometric Knowledge Distillation for Information Retrieval
S Kim, A S Rawat, M Zaheer, S Jayasumana, V Sadhanala, W Jitkrittum, A K Menon, R Fergus, S Kumar
[Google LLC]
EmbedDistill: 面向信息检索的几何知识蒸馏
要点:
-
提出用于 IR 的 EmbedDistill 蒸馏方法,使教师和学生模型的嵌入空间一致,以获得更好的性能; -
证明了 EmbedDistill 将一个 DE 模型蒸馏成另一个 DE 模型的有效性,减少了延迟并利用了教师的高质量文档索引; -
通过查询生成技术和嵌入匹配提高了蒸馏后的学生模型的性能。
一句话总结:
EmbedDistill 是一种用于信息检索(IR)的新蒸馏方法,将教师和学生模型的嵌入空间对齐,提高了实际部署的质量和计算收益,并优于现有方法。
摘要:
大型神经模型(如Transformer)在信息检索(IR)方面取得了最先进的性能。本文旨在改进蒸馏方法,为在实践中部署这类模型铺平道路。所提出的蒸馏方法支持检索和重排阶段,关键是利用大型教师模型所学到的查询和文档之间的相对几何。它在两个方面超越了IR文献中现有的蒸馏方法,这些方法仅依赖于教师在训练数据上的标量分数:通过嵌入匹配提供关于局部几何的更强信号,并通过查询生成实现对数据流形的更好覆盖。嵌入匹配提供了一个更强的信号来调整教师和学生模型的表示。同时,查询生成可以探索数据流形,以减少训练数据稀少时师生之间的差异。所提出的蒸馏方法在理论上是合理的,适用于双编码器(DE)和交叉编码器(CE)模型。此外,为了通过嵌入匹配将CE模型蒸馏成DE模型,为CE模型提出了一种新的基于双池化的评分器,有利于蒸馏方便的嵌入几何,特别是对于DE学生模型。
Large neural models (such as Transformers) achieve state-of-the-art performance for information retrieval (IR). In this paper, we aim to improve distillation methods that pave the way for the deployment of such models in practice. The proposed distillation approach supports both retrieval and re-ranking stages and crucially leverages the relative geometry among queries and documents learned by the large teacher model. It goes beyond existing distillation methods in the IR literature, which simply rely on the teacher’s scalar scores over the training data, on two fronts: providing stronger signals about local geometry via embedding matching and attaining better coverage of data manifold globally via query generation. Embedding matching provides a stronger signal to align the representations of the teacher and student models. At the same time, query generation explores the data manifold to reduce the discrepancies between the student and teacher where training data is sparse. Our distillation approach is theoretically justified and applies to both dual encoder (DE) and cross-encoder (CE) models. Furthermore, for distilling a CE model to a DE model via embedding matching, we propose a novel dual pooling-based scorer for the CE model that facilitates a distillation-friendly embedding geometry, especially for DE student models.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.12005

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
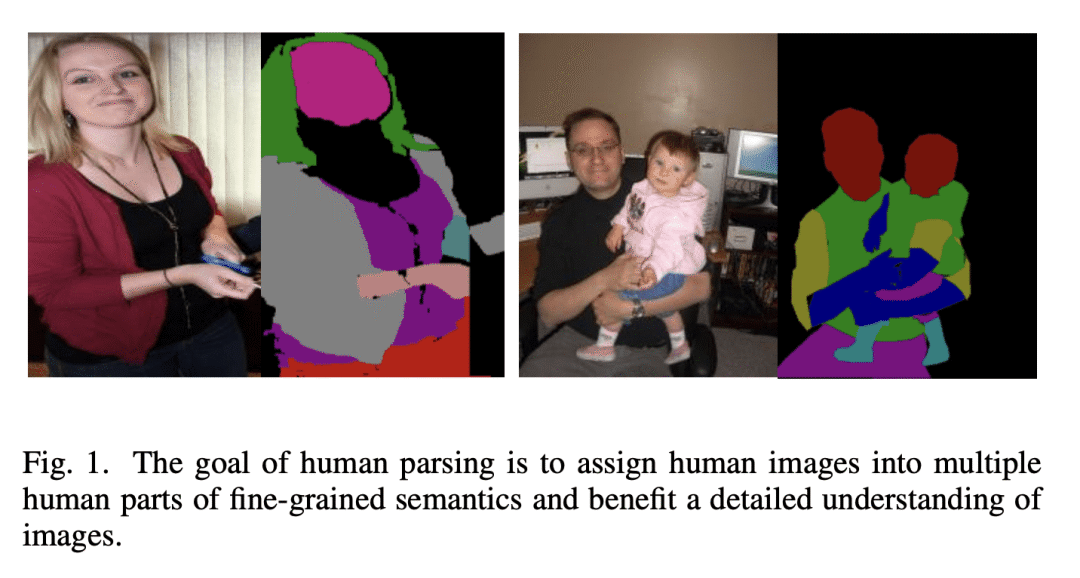
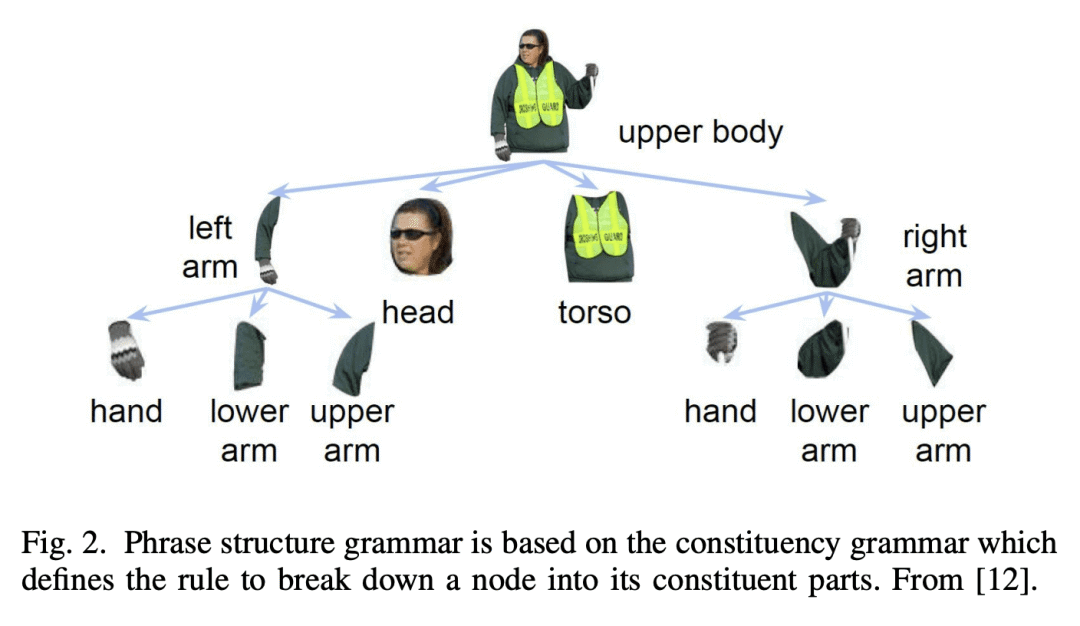
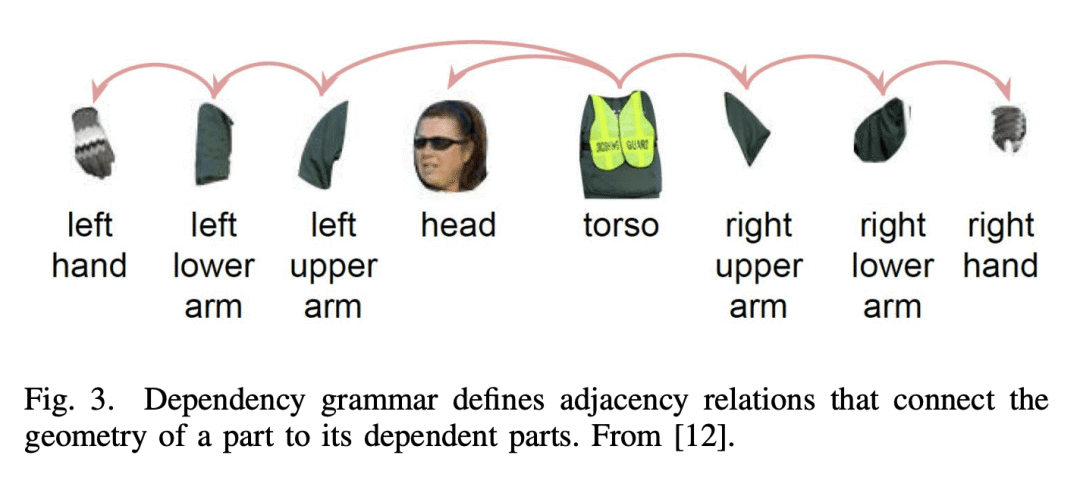
[CV] Deep Learning for Human Parsing: A Survey
X Zhang, X Zhu, M Tang, Z Lei
[Chinese Academy of Sciences]
深度学习人体解析综述
要点:
-
概述了2022年前提出的基于深度学习的人体解析算法; -
提供了对人体解析方法的见解,包括网络架构、训练数据、主要贡献和限制; -
回顾了流行的人体解析数据集,并对所回顾的方法在流行基准上的性能进行了比较总结。
一句话总结:
全面概述了用于人体解析的最先进的深度学习方法,分为五个类别,包括对流行数据集、性能比较和未来研究方向的总结。
Human parsing is a key topic in image processing with many applications, such as surveillance analysis, human-robot interaction, person search, and clothing category classification, among many others. Recently, due to the success of deep learning in computer vision, there are a number of works aimed at developing human parsing algorithms using deep learning models. As methods have been proposed, a comprehensive survey of this topic is of great importance. In this survey, we provide an analysis of state-of-the-art human parsing methods, covering a broad spectrum of pioneering works for semantic human parsing. We introduce five insightful categories: (1) structure-driven architectures exploit the relationship of different human parts and the inherent hierarchical structure of a human body, (2) graph-based networks capture the global information to achieve an efficient and complete human body analysis, (3) context-aware networks explore useful contexts across all pixel to characterize a pixel of the corresponding class, (4) LSTM-based methods can combine short-distance and long-distance spatial dependencies to better exploit abundant local and global contexts, and (5) combined auxiliary information approaches use related tasks or supervision to improve network performance. We also discuss the advantages/disadvantages of the methods in each category and the relationships between methods in different categories, examine the most widely used datasets, report performances, and discuss promising future research directions in this area.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.12416

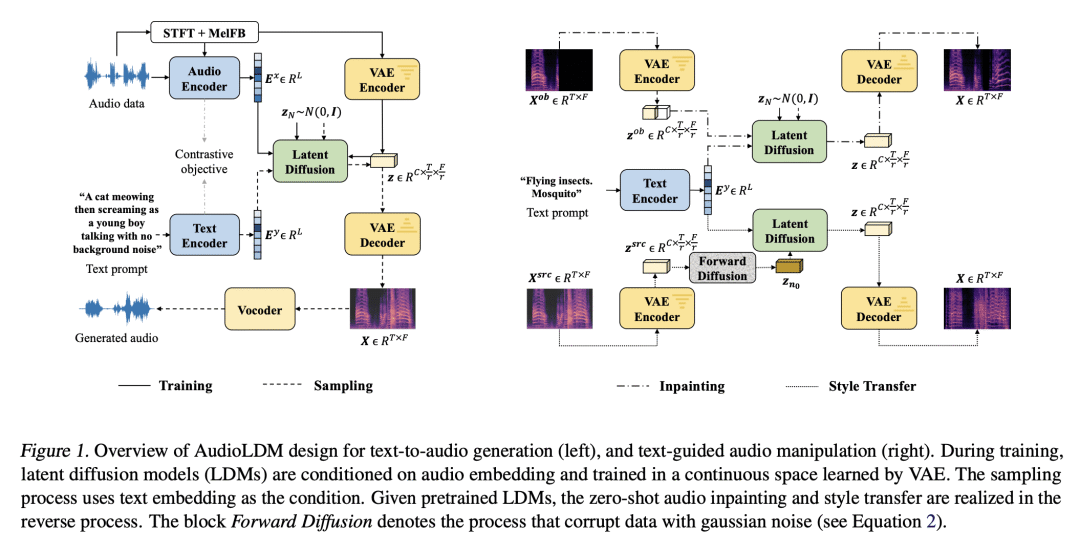
[AS]《AudioLDM: Text-to-Audio Generation with Latent Diffusion Models》H Liu, Z Chen, Y Yuan, X Mei, X Liu, D Mandic, W Wang, M D. Plumbley
[University of Surrey & Imperial College London]
AudioLDM: 基于潜扩散模型的文本到音频生成
要点:
-
提出第一个用于文本-音频(TTA)生成的连续潜扩散模型(LDM),在主观评价和客观指标方面都优于现有方法; -
利用对比语言-音频预训练(CLAP)潜空间,在不使用语言-音频对训练 LDM 模型的情况下实现了TTA生成; -
证明了在LDM训练中只使用音频数据可以获得一个高质量和计算高效的TTA系统。
一句话总结:
AudioLDM是一个基于对比语言-音频预训练(CLAP)和潜扩散模型(LDMs)的文本-音频(TTA)生成系统,具有更好的生成质量、计算效率和零样本文本指导音频操纵能力。
Text-to-audio (TTA) system has recently gained attention for its ability to synthesize general audio based on text descriptions. However, previous studies in TTA have limited generation quality with high computational costs. In this study, we propose AudioLDM, a TTA system that is built on a latent space to learn the continuous audio representations from contrastive language-audio pretraining (CLAP) latents. The pretrained CLAP models enable us to train LDMs with audio embedding while providing text embedding as a condition during sampling. By learning the latent representations of audio signals and their compositions without modeling the cross-modal relationship, AudioLDM is advantageous in both generation quality and computational efficiency. Trained on AudioCaps with a single GPU, AudioLDM achieves state-of-the-art TTA performance measured by both objective and subjective metrics (e.g., frechet distance). Moreover, AudioLDM is the first TTA system that enables various text-guided audio manipulations (e.g., style transfer) in a zero-shot fashion. Our implementation and demos are available at this https URL.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.12503


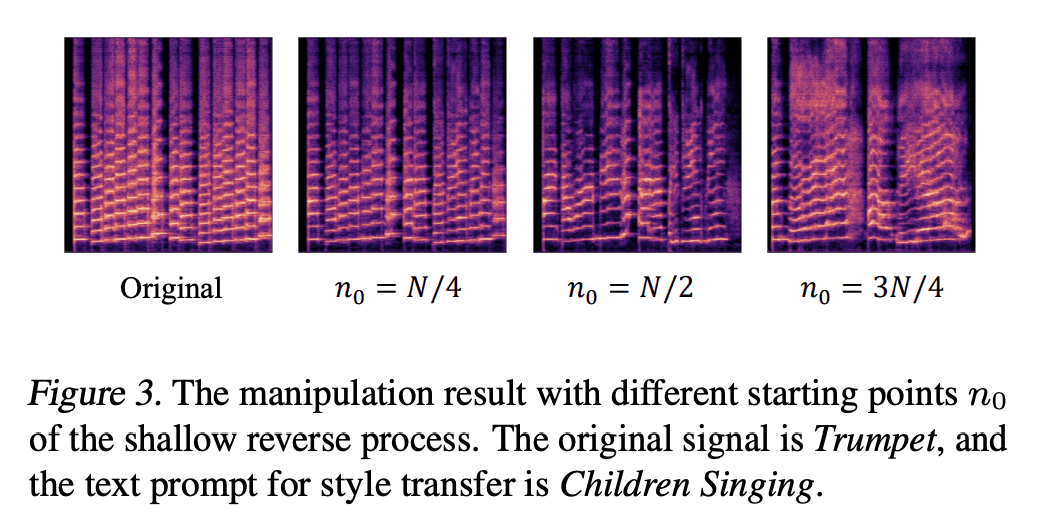
[CL] In-Context Retrieval-Augmented Language Models
O Ram, Y Levine, I Dalmedigos, D Muhlgay, A Shashua, K Leyton-Brown, Y Shoham
[AI21 Labs]
上下文检索增强语言模型
要点:
-
提出上下文检索增强语言模型(RALM)的概念; -
解释上下文RALM与现有的RALM方法有何不同; -
证据表明,上下文RALM使用通用检索器可以显著提高语言建模性能。
一句话总结:
提出上下文检索-增强语言建模(RALM),在不改变语言模型架构的情况下,通过对输入的相关文档进行预处理来改善语言建模,并提供了一种来源贡献机制。
Retrieval-Augmented Language Modeling (RALM) methods, that condition a language model (LM) on relevant documents from a grounding corpus during generation, have been shown to significantly improve language modeling while also providing a natural source attribution mechanism. Existing RALM approaches focus on modifying the LM architecture in order to facilitate the incorporation of external information, significantly complicating deployment. This paper proposes an under-explored alternative, which we dub In-Context RALM: leaving the LM architecture unchanged and prepending grounding documents to the input. We show that in-context RALM which uses off-the-shelf general purpose retrievers provides surprisingly large LM gains across model sizes and diverse corpora. We also demonstrate that the document retrieval and ranking mechanism can be specialized to the RALM setting to further boost performance. We conclude that in-context RALM has considerable potential to increase the prevalence of LM grounding, particularly in settings where a pretrained LM must be used without modification or even via API access. To that end, we make our code publicly available.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.00083

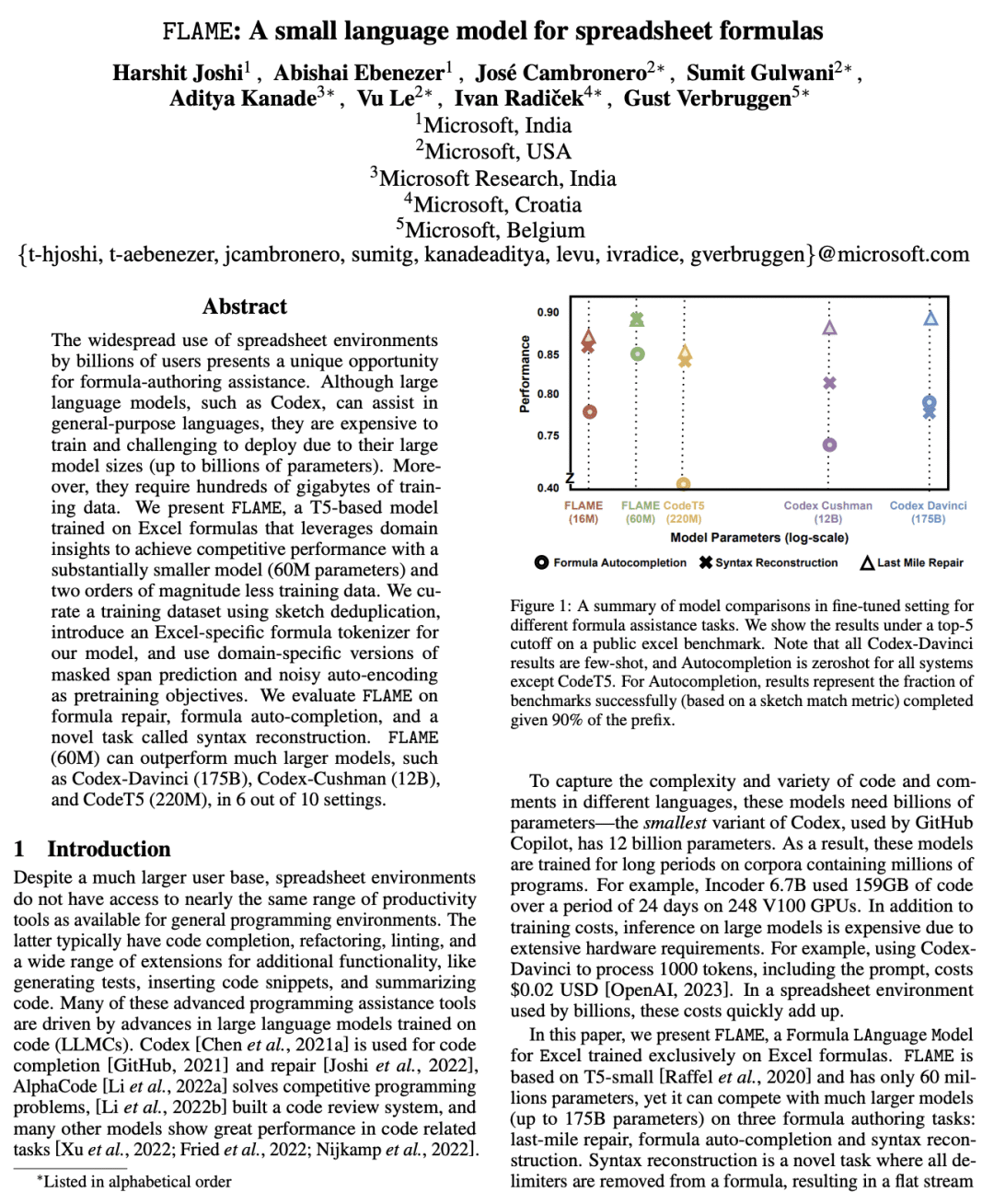
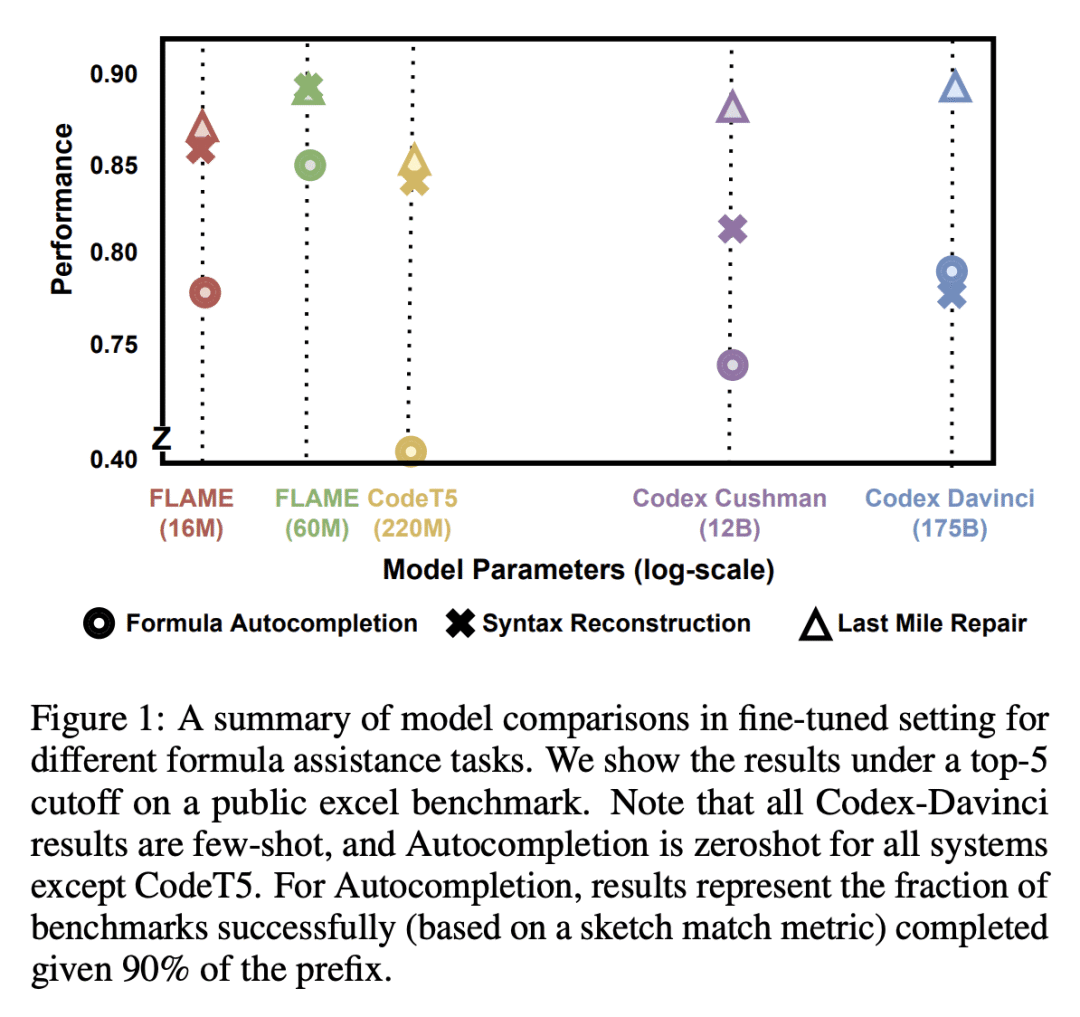
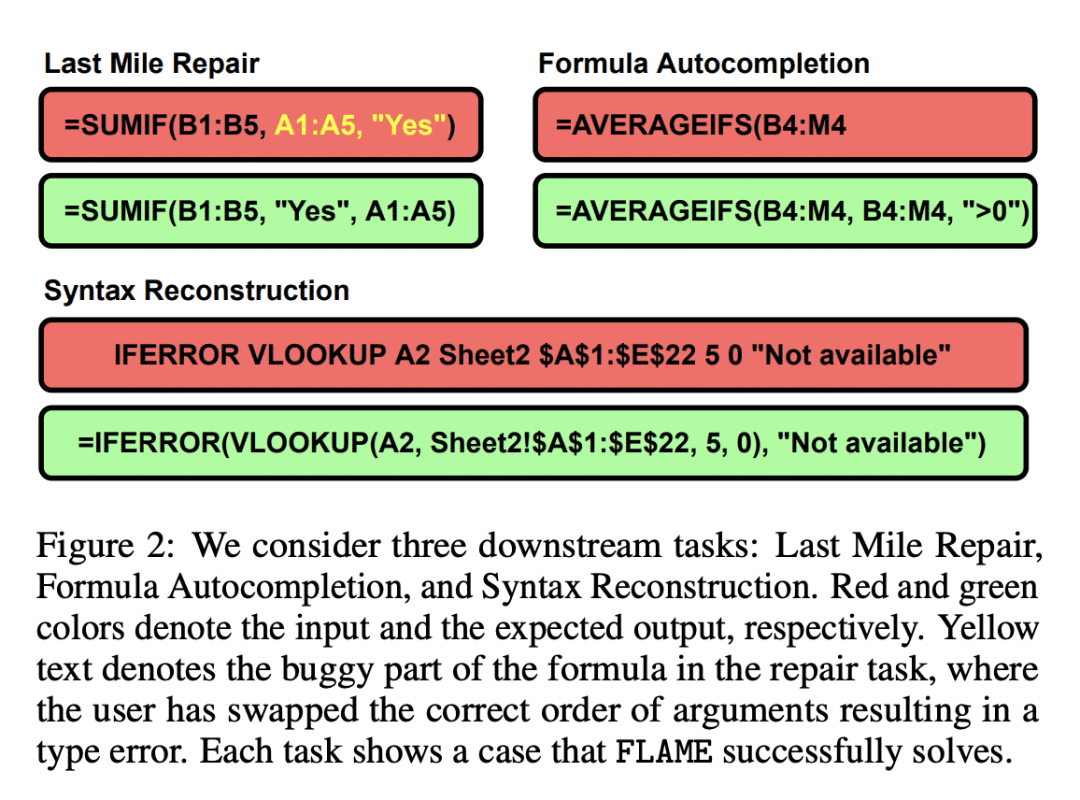
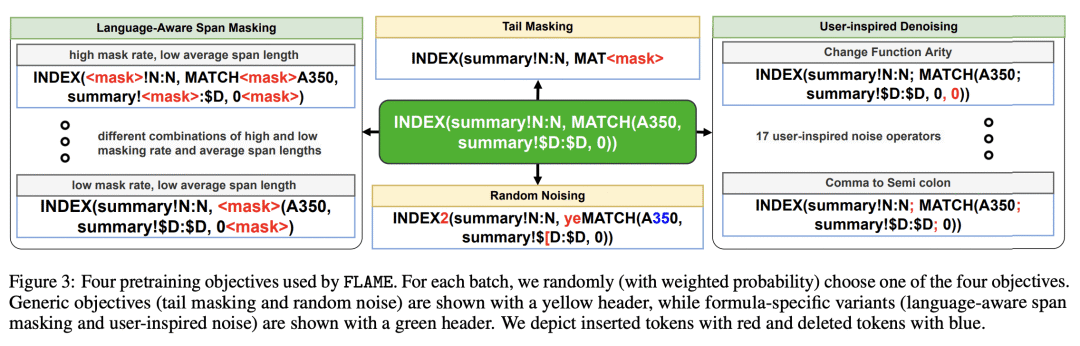
[LG] FLAME: A small language model for spreadsheet formulas
H Joshi, A Ebenezer, J Cambronero, S Gulwani, A Kanade, V Le, I Radiček, G Verbruggen
[Microsoft]
FLAME: 面向电子表格公式的小型语言模型
要点:
-
FLAME是一个小型(60M参数)基于 T5 的 Excel 公式语言模型,在数据整理、Token 化和预训练目标中捕捉到了特定域的属性; -
FLAME 在最后阶段修复、公式自动补全和语法重建任务的10个设置中,有6个优于较大的模型; -
FLAME 是第一个专门为 Excel 公式设计的语言模型,其有效性通过广泛的评估和与其他模型的比较得到了证明。
一句话总结:
FLAME 是一个专门为 Excel 电子表格公式设计的小型(60M参数)语言模型,利用特定域的数据整理、Token化和预训练目标,在包括最后阶段修复、自动补全和语法重建的公式辅助任务中取得有竞争力的性能。
The widespread use of spreadsheet environments by billions of users presents a unique opportunity for formula-authoring assistance. Although large language models, such as Codex, can assist in general-purpose languages, they are expensive to train and challenging to deploy due to their large model sizes (up to billions of parameters). Moreover, they require hundreds of gigabytes of training data. We present FLAME, a T5-based model trained on Excel formulas that leverages domain insights to achieve competitive performance with a substantially smaller model (60M parameters) and two orders of magnitude less training data. We curate a training dataset using sketch deduplication, introduce an Excel-specific formula tokenizer for our model, and use domain-specific versions of masked span prediction and noisy auto-encoding as pretraining objectives. We evaluate FLAME on formula repair, formula auto-completion, and a novel task called syntax reconstruction. FLAME (60M) can outperform much larger models, such as Codex-Davinci (175B), Codex-Cushman (12B), and CodeT5 (220M), in 6 out of 10 settings.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.13779





 ufabet
มีเกมให้เลือกเล่นมากมาย: เกมเดิมพันหลากหลาย ครบทุกค่ายดัง
ufabet
มีเกมให้เลือกเล่นมากมาย: เกมเดิมพันหลากหลาย ครบทุกค่ายดัง

