引言
自然语言处理 (NLP) 领域的进展日新月异,你方唱罢我登场。因此,在实际场景中,针对特定的任务,我们经常需要对不同的语言模型进行比较,以寻找最适合的模型。本文主要比较 3 个模型: RoBERTa、Mistral-7B 及 Llama-2-7B。我们用它们来解决一个常见问题 —— 对灾难相关的推文进行分类。值得注意的是,Mistral 和 Llama 2 是 70 亿参数的大模型。相形之下,RoBERTa-large (355M 参数) 只是一个小模型,我们用它作为比较的基线。
本文,我们使用 PEFT (Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning,参数高效微调) 技术: LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation,低秩适配) 来微调带序列分类任务头的预训练模型。LoRA 旨在显著减少可训参数量,同时保持强大的下游任务性能。
本文的主要目标是通过对 Hugging Face 的三个预训练模型进行 LoRA 微调,使之适用于序列分类任务。这三个预训练模型分别是: meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf、mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1 及 roberta-large。
使用的硬件
- 节点数: 1
- 每个节点的 GPU 数: 1
- GPU 类型: A6000
- GPU 显存: 48GB
目标
- 使用 LoRA PEFT 方法对预训练 LLM 进行微调。
- 了解如何使用 Hugging Face 的各种 API (transformers、peft 以及 datasets)。
- 使用 Weights & Biases 进行超参调优以及实验日志记录。
软件依赖
datasets
evaluate
peft
scikit-learn
torch
transformers
wandb
注意: 要准确重现本文结果,请注意确保软件版本与 wandb 报告 的一致。
预训练模型
RoBERTa
RoBERTa (Robustly Optimized BERT Approach) 是 Meta AI 研究团队提出的改进版 BERT 模型。BERT 是一种基于 transformer 的语言模型,其基于自注意力机制对单词进行上下文感知的表征,并基于掩码语言模型目标进行训练。请注意,BERT 作为编码器模型,仅可用于自然语言理解任务 (例如序列分类和词元分类)。
RoBERTa 是一种流行的可微调模型,很适合作为我们实验的基线。欲了解更多信息,你可以查阅其 Hugging Face 模型卡。
Llama 2
Llama 2 (Large Language Model Meta AI) 是 Meta AI 推出的一系列大语言模型 (LLM),其模型大小各异,参数量从 70 亿到 650 亿不等。
Llama 2 是一种基于 transformer 解码器架构的自回归语言模型。Llama 2 接受单词序列作为输入,并基于滑动窗口迭代预测下一个词元,从而实现文本生成的功能。
Llama 2 的架构与 GPT-3 等模型略有不同。举几个例子,Llama 2 采用 SwiGLU 激活函数而不是 ReLU,另外其位置嵌入使用的是旋转位置嵌入而不是可训绝对位置嵌入。
最近发布的 Llama 2 还对架构进行了改进,其将支持的最大上下文长度扩展到 4096 个词元,并使用分组查询注意 (grouped-query attention,GQA) 解码机制来更好地利用长序列。
Mistral 7B
Mistral 7B v0.1 有 73 亿个参数,是 Mistral AI 推出的第一个 LLM。
Mistral 7B 架构使用的新技术主要有:
- 滑窗注意力: 用基于滑动窗口的注意力替换完整注意力 (平方级计算成本),其中每个词元最多可以关注上一层的 4096 个词元 (线性计算成本)。这样,多层以后,Mistral 7B 的实际关注词元数会叠加,因此更高层的注意力实际关注的总历史词元数会超过 4096。
- 分组查询注意力: Llama 2 也使用了该技术,其通过缓存先前解码的词元的键向量和值向量来优化推理过程 (减少处理时间)。
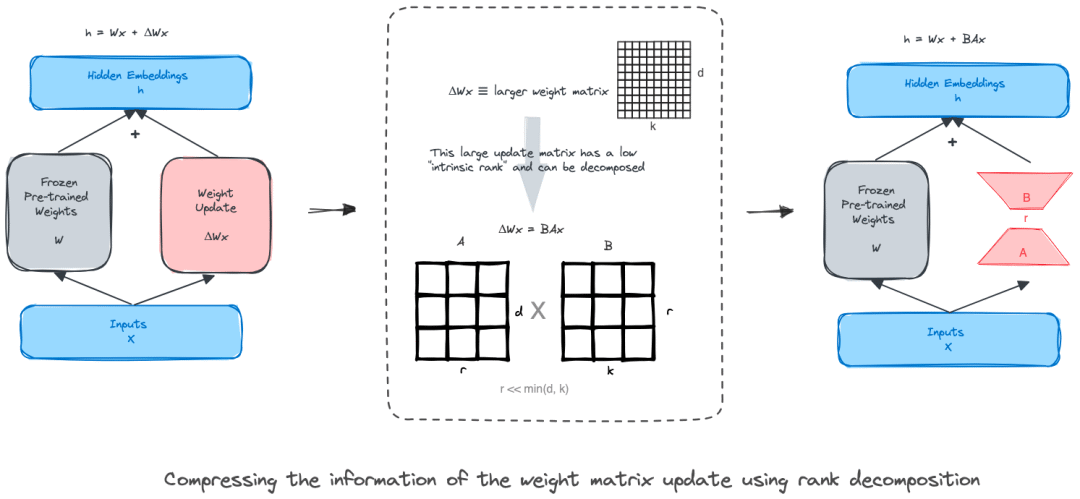
LoRA
PEFT (Parameter Efficient Fine-Tuning,参数高效微调) 包含 p-tuning、前缀微调 (prefix-tuning) 、IA3、适配器微调以及 LoRA 等一系列技术,其旨在通过仅微调大模型的一个小参数集,就能达到全模型微调的性能水平。
LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation,低阶适配) 的方法与添加适配层类似。其主要目标是减少模型的可训参数量。LoRA 的主要做法是冻结预训练权重,仅更新一个新增的低秩矩阵。
环境设置
RoBERTa 支持的最大序列长度为 512,为公平起见,对所有模型,我们统一设定 MAX_LEN=512 。
MAX_LEN = 512
roberta_checkpoint = "roberta-large"
mistral_checkpoint = "mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1"
llama_checkpoint = "meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf"
数据准备
数据加载
从 Hugging Face 加载数据集:
from datasets import load_dataset
dataset = load_dataset("mehdiiraqui/twitter_disaster")
将数据集分为训练集和验证集,同时加载测试集:
from datasets import Dataset
# 将数据集的训练集划分为训练集和验证集
data = dataset['train'].train_test_split(train_size=0.8, seed=42)
# 把划分而得的测试集重命名为验证集
data['val'] = data.pop("test")
# 将原数据集的测试集仍作为测试集
data['test'] = dataset['test']
以下是数据集概览:
DatasetDict({
train: Dataset({
features: ['id', 'keyword', 'location', 'text', 'target'],
num_rows: 6090
})
val: Dataset({
features: ['id', 'keyword', 'location', 'text', 'target'],
num_rows: 1523
})
test: Dataset({
features: ['id', 'keyword', 'location', 'text', 'target'],
num_rows: 3263
})
})
首先,检查一下数据分布:
import pandas as pd
data[‘train’].to_pandas().info()
data[‘test’].to_pandas().info()
- 训练集
RangeIndex: 7613 entries, 0 to 7612
Data columns (total 5 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 id 7613 non-null int64
1 keyword 7552 non-null object
2 location 5080 non-null object
3 text 7613 non-null object
4 target 7613 non-null int64
dtypes: int64(2), object(3)
memory usage: 297.5+ KB
- 测试集
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 3263 entries, 0 to 3262
Data columns (total 5 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 id 3263 non-null int64
1 keyword 3237 non-null object
2 location 2158 non-null object
3 text 3263 non-null object
4 target 3263 non-null int64
dtypes: int64(2), object(3)
memory usage: 127.6+ KB
训练集中标签分布情况:
target
0 4342
1 3271
Name: count, dtype: int64
由于类别不平衡,我们计算一下正负类权重,以用于稍后的损失计算:
pos_weights = len(data['train'].to_pandas()) / (2 * data['train'].to_pandas().target.value_counts()[1])
neg_weights = len(data['train'].to_pandas()) / (2 * data['train'].to_pandas().target.value_counts()[0])
计算出的权重为:
POS_WEIGHT, NEG_WEIGHT = (1.1637114032405993, 0.8766697374481806)
接着,我们计算文本序列的最大长度:
# 字符数
max_char = data['train'].to_pandas()['text'].str.len().max()
# 词数
max_words = data['train'].to_pandas()['text'].str.split().str.len().max()The maximum number of characters is 152.
The maximum number of words is 31.
数据处理
以一条训练数据为例:
data['train'][0]{'id': 5285,
'keyword': 'fear',
'location': 'Thibodaux, LA',
'text': 'my worst fear. https://t.co/iH8UDz8mq3',
'target': 0}
该数据中包括关键字、位置和推文。为了简单起见,我们选择 text 特征作为 LLM 的唯一输入。
本阶段的目标是为 LLM 微调准备所需的 Hugging Face 格式的训练集、验证集和测试集。然后是定义用于训练的词元数据集,使用合适的分词器将 text 特征转换为词元 id 和注意力掩码序列这两个张量。由于每个模型都有其特定的分词器,因此我们需要生成三个不同的数据集,每个模型一个。
我们首先定义 RoBERTa 模型的数据加载器:
- 加载与分词:
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
roberta_tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(roberta_checkpoint, add_prefix_space=True)
注意: RoBERTa 分词器经过训练已将空格视为词元的一部分。因此,如果句子的第一个单词前面没有空格,则其编码会有所不同。为了确保第一个单词包含空格,我们设置 add_prefix_space=True 。同时,为了保持三个模型的预处理一致,我们将 Llama 2 和 Mistral 7B 的相应参数也设为 True 。
- 定义每条数据的预处理函数:
def roberta_preprocessing_function(examples):
return roberta_tokenizer(examples['text'], truncation=True, max_length=MAX_LEN)
将预处理函数应用于训练数据集的第一条数据,我们得到了分词后的输入 ( input_ids ) 及其注意力掩码:
roberta_preprocessing_function(data['train'][0]){'input_ids': [0, 127, 2373, 2490, 4, 1205, 640, 90, 4, 876, 73, 118, 725, 398, 13083, 329, 398, 119, 1343, 246, 2], 'attention_mask': [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]}
- 现在,将预处理函数应用于整个数据集:
col_to_delete = ['id', 'keyword','location', 'text']
# 删除不需要的列,并应用预处理函数
roberta_tokenized_datasets = data.map(roberta_preprocessing_function, batched=True, remove_columns=col_to_delete)
# 按照 HuggingFace 的要求,将 `target` 列 重命名为 `label` 列
roberta_tokenized_datasets = roberta_tokenized_datasets.rename_column("target", "label")
# 数据集格式设为 "torch"
roberta_tokenized_datasets.set_format("torch")
注意: 我们从数据中删除了不需要的列: id 、 keyword 、 location 及 text 。删除 text 的原因是我们已经将其转换为输入 id 和注意力掩码:
分词后的训练数据集中的数据如下:
roberta_tokenized_datasets['train'][0]{'label': tensor(0),
'input_ids': tensor([ 0, 127, 2373, 2490, 4, 1205, 640, 90, 4, 876,
73, 118, 725, 398, 13083, 329, 398, 119, 1343, 246,
2]),
'attention_mask': tensor([1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1])}
- 为了生成训练 batch 数据,我们还需要对给定 batch 中的序列进行填充,以使 batch 中所有序列的长度都等于本 batch 最长序列的长度。为此,我们使用了
DataCollatorWithPadding类:
# 数据整理器将所有数据统一填充至 batch 内最长序列的长度
from transformers import DataCollatorWithPadding
roberta_data_collator = DataCollatorWithPadding(tokenizer=roberta_tokenizer)
用相同的流程为 Mistral 7B 和 Llama 2 模型准备数据:
注意 Llama 2 和 Mistral 7B 没有默认的 pad_token_id ,我们将其设为 eos_token_id 。
- Mistral 7B:
# 加载 Mistral 7B 分词器
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, DataCollatorWithPadding
mistral_tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(mistral_checkpoint, add_prefix_space=True)
mistral_tokenizer.pad_token_id = mistral_tokenizer.eos_token_id
mistral_tokenizer.pad_token = mistral_tokenizer.eos_token
def mistral_preprocessing_function(examples):
return mistral_tokenizer(examples[‘text’], truncation=True, max_length=MAX_LEN)
mistral_tokenized_datasets = data.map(mistral_preprocessing_function, batched=True, remove_columns=col_to_delete)
mistral_tokenized_datasets = mistral_tokenized_datasets.rename_column(“target”, “label”)
mistral_tokenized_datasets.set_format(“torch”)
# 序列填充
mistral_data_collator = DataCollatorWithPadding(tokenizer=mistral_tokenizer)
- Llama 2:
# 加载 Llama 2 分词器
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, DataCollatorWithPadding
llama_tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(llama_checkpoint, add_prefix_space=True)
llama_tokenizer.pad_token_id = llama_tokenizer.eos_token_id
llama_tokenizer.pad_token = llama_tokenizer.eos_token
def llama_preprocessing_function(examples):
return llama_tokenizer(examples[‘text’], truncation=True, max_length=MAX_LEN)
llama_tokenized_datasets = data.map(llama_preprocessing_function, batched=True, remove_columns=col_to_delete)
llama_tokenized_datasets = llama_tokenized_datasets.rename_column(“target”, “label”)
llama_tokenized_datasets.set_format(“torch”)
# 序列填充
llama_data_collator = DataCollatorWithPadding(tokenizer=llama_tokenizer)
至此,我们已经准备好了分词后的数据集,下一节我们将讨论如何加载预训练 LLM 检查点以及如何设置 LoRA 权重。
模型
RoBERTa
为分类任务加载 RoBERTa 检查点
我们使用 Hugging Face AutoModelForSequenceClassification 类加载带有序列分类头的预训练 RoBERTa 模型:
from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification
roberta_model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(roberta_checkpoint, num_labels=2)
RoBERTa 分类器的 LoRA 设置
我们为 RoBERTa 分类器设置 LoRA 参数:
- TaskType: 序列分类
- r(rank): 分解矩阵的秩
- lora_alpha: 用于对习得权重进行缩放的 alpha 参数。LoRA 论文建议将 alpha 固定为 16
- lora_dropout: LoRA 层的 Dropout 概率
- bias: 是否向 LoRA 层添加偏置
以下代码使用了 LoRA 论文 的推荐设置。后文 我们还将用 wandb 对这些超参进行调优。
from peft import get_peft_model, LoraConfig, TaskType
roberta_peft_config = LoraConfig(
task_type=TaskType.SEQ_CLS, r=2, lora_alpha=16, lora_dropout=0.1, bias="none",
)
roberta_model = get_peft_model(roberta_model, roberta_peft_config)
roberta_model.print_trainable_parameters()
可以看到,可训参数量仅占 RoBERTa 模型参数量的 0.64%:
trainable params: 2,299,908 || all params: 356,610,052 || trainable%: 0.6449363911929212
Mistral
为分类任务加载检查点
加载带有序列分类头的预训练 Mistral-7B 模型:
from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification
import torch
mistral_model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(
pretrained_model_name_or_path=mistral_checkpoint,
num_labels=2,
device_map="auto"
)
设置填充词元 id,因为 Mistral 7B 没有默认填充词元。
mistral_model.config.pad_token_id = mistral_model.config.eos_token_id
Mistral 7B 分类器的 LoRA 设置
对 Mistral 7B 模型而言,我们需要指定 target_modules (我们将其指定为注意力模块的查询向量映射层和值向量映射层):
from peft import get_peft_model, LoraConfig, TaskType
mistral_peft_config = LoraConfig(
task_type=TaskType.SEQ_CLS, r=2, lora_alpha=16, lora_dropout=0.1, bias=“none”,
target_modules=[
“q_proj”,
“v_proj”,
],
)
mistral_model = get_peft_model(mistral_model, mistral_peft_config)
mistral_model.print_trainable_parameters()
可训参数量仅占 Mistral 模型参数量的 0.024%:
trainable params: 1,720,320 || all params: 7,112,380,416 || trainable%: 0.02418768259540745
Llama 2
为分类任务加载检查点
加载带有序列分类头的预训练 Llama 2 模型。
from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification
import torch
llama_model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(
pretrained_model_name_or_path=llama_checkpoint,
num_labels=2,
device_map="auto",
offload_folder="offload",
trust_remote_code=True
)
设置填充词元 id,因为 Llama 2 没有默认填充词元。
llama_model.config.pad_token_id = llama_model.config.eos_token_id
Llama 2 分类器的 LoRA 设置
使用与 Mistral 相同的 LoRA 参数:
from peft import get_peft_model, LoraConfig, TaskType
llama_peft_config = LoraConfig(
task_type=TaskType.SEQ_CLS, r=16, lora_alpha=16, lora_dropout=0.05, bias="none",
target_modules=[
"q_proj",
"v_proj",
],
)
llama_model = get_peft_model(llama_model, llama_peft_config)
llama_model.print_trainable_parameters()
可训参数量仅占 Llama 2 模型参数量的 0.12%:
trainable params: 8,404,992 || all params: 6,615,748,608 || trainable%: 0.1270452143516515
至此,我们定义了用于训练的词元数据集及 LoRA 设置。下面,我们介绍如何使用 Hugging Face 的 Trainer 类启动训练。
设置 Trainer
评估指标
首先,我们定义用于对三个模型的性能进行比较的指标: F1 分数、召回率、精确度和准确度:
import evaluate
import numpy as np
def compute_metrics(eval_pred):
# HF `evaluate` 包已支持我们所要的所有指标
precision_metric = evaluate.load(“precision”)
recall_metric = evaluate.load(“recall”)
f1_metric= evaluate.load(“f1”)
accuracy_metric = evaluate.load(“accuracy”)
logits, labels = eval_pred
# eval_pred 是模型返回的预测值和实际值元组
predictions = np.argmax(logits, axis=-1)
precision = precision_metric.compute(predictions=predictions, references=labels)[“precision”]
recall = recall_metric.compute(predictions=predictions, references=labels)[“recall”]
f1 = f1_metric.compute(predictions=predictions, references=labels)[“f1”]
accuracy = accuracy_metric.compute(predictions=predictions, references=labels)[“accuracy”]
# `Trainer` 要求将指标组织为一个字典,其键为指标名,值为分数。
return {“precision”: precision, “recall”: recall, “f1-score”: f1, ‘accuracy’: accuracy}
基于加权损失的自定义 Trainer
前文提到,数据集正负类分布并不平衡。因此,我们用加权交叉熵损失来训练模型以解决这个问题。Trainer 类本身的实现中不支持自定义损失,因为它期望直接从模型的输出中获取损失。
因此,我们需要定义一个自定义的 WeightedCELossTrainer ,以重写 compute_loss 方法,该方法可以根据模型的预测和标签计算加权交叉熵损失:
from transformers import Trainer
class WeightedCELossTrainer(Trainer):
def compute_loss(self, model, inputs, return_outputs=False):
labels = inputs.pop(“labels”)
# Get model’s predictions
outputs = model(**inputs)
logits = outputs.get(“logits”)
# Compute custom loss
loss_fct = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight=torch.tensor([neg_weights, pos_weights], device=model.device, dtype=logits.dtype))
loss = loss_fct(logits.view(-1, self.model.config.num_labels), labels.view(-1))
return (loss, outputs) if return_outputs else loss
Trainer 设置
我们为三个模型分别设置训练超参及训练器。
RoBERTa
第一步,把模型搬到 GPU 设备上。
roberta_model = roberta_model.cuda()
roberta_model.device()
It will print the following:
device(type='cuda', index=0)
然后,设置训练超参:
from transformers import TrainingArguments
lr = 1e-4
batch_size = 8
num_epochs = 5
training_args = TrainingArguments(
output_dir=“roberta-large-lora-token-classification”,
learning_rate=lr,
lr_scheduler_type= “constant”,
warmup_ratio= 0.1,
max_grad_norm= 0.3,
per_device_train_batch_size=batch_size,
per_device_eval_batch_size=batch_size,
num_train_epochs=num_epochs,
weight_decay=0.001,
evaluation_strategy=“epoch”,
save_strategy=“epoch”,
load_best_model_at_end=True,
report_to=“wandb”,
fp16=False,
gradient_checkpointing=True,
)
最后,我们将模型、训练超参和词元数据集一起作为参数来实例化一个 RoBERTa 训练器:
roberta_trainer = WeightedCELossTrainer(
model=roberta_model,
args=training_args,
train_dataset=roberta_tokenized_datasets['train'],
eval_dataset=roberta_tokenized_datasets["val"],
data_collator=roberta_data_collator,
compute_metrics=compute_metrics
)
Mistral-7B
与 RoBERTa 类似,我们用如下代码初始化 WeightedCELossTrainer :
from transformers import TrainingArguments, Trainer
mistral_model = mistral_model.cuda()
lr = 1e-4
batch_size = 8
num_epochs = 5
training_args = TrainingArguments(
output_dir=“mistral-lora-token-classification”,
learning_rate=lr,
lr_scheduler_type= “constant”,
warmup_ratio= 0.1,
max_grad_norm= 0.3,
per_device_train_batch_size=batch_size,
per_device_eval_batch_size=batch_size,
num_train_epochs=num_epochs,
weight_decay=0.001,
evaluation_strategy=“epoch”,
save_strategy=“epoch”,
load_best_model_at_end=True,
report_to=“wandb”,
fp16=True,
gradient_checkpointing=True,
)
mistral_trainer = WeightedCELossTrainer(
model=mistral_model,
args=training_args,
train_dataset=mistral_tokenized_datasets[‘train’],
eval_dataset=mistral_tokenized_datasets[“val”],
data_collator=mistral_data_collator,
compute_metrics=compute_metrics
)
注意,我们需要将 fp16 设为 True 以启用半精度训练。主要原因是 Mistral-7B 很大,如果使用 fp32 精度,其权重无法放进单块 GPU 的显存 (48GB) 中。
Llama 2
与 Mistral 7B 类似,我们用如下代码定义训练器:
from transformers import TrainingArguments, Trainer
llama_model = llama_model.cuda()
lr = 1e-4
batch_size = 8
num_epochs = 5
training_args = TrainingArguments(
output_dir=“llama-lora-token-classification”,
learning_rate=lr,
lr_scheduler_type= “constant”,
warmup_ratio= 0.1,
max_grad_norm= 0.3,
per_device_train_batch_size=batch_size,
per_device_eval_batch_size=batch_size,
num_train_epochs=num_epochs,
weight_decay=0.001,
evaluation_strategy=“epoch”,
save_strategy=“epoch”,
load_best_model_at_end=True,
report_to=“wandb”,
fp16=True,
gradient_checkpointing=True,
)
llama_trainer = WeightedCELossTrainer(
model=llama_model,
args=training_args,
train_dataset=llama_tokenized_datasets[‘train’],
eval_dataset=llama_tokenized_datasets[“val”],
data_collator=llama_data_collator,
compute_metrics=compute_metrics
)
超参调优
我们用 Wandb Sweep API 通过贝叶斯搜索策略来进行超参调优 (30 次运行),待调优的超参搜索空间如下:
方法指标lora_alphalora_biaslora_dropoutlora_ranklrmax_lengthbayes目标: maximize分布: categorical分布: categorical分布: uniform分布: categorical分布: uniform分布: categorical
目标名: eval/f1-score取值集合:
-16
-32
-64取值集合: None-最大值: 0.1
-最小值: 0取值集合:
-4
-8
-16
-32-最大值: 2e-04
-最小值: 1e-05取值集合: 512
欲了解更多信息,可以查看 资源 一节中的 Wandb 实验报告。
结果
模型F1 分数训练时间内存消耗可训参数量RoBERTa0.8077538 秒GPU1: 9.1 GB
GPU2: 8.3 GB0.64%Mistral 7B0.73642030 秒GPU1: 29.6 Gb
GPU2: 29.5 GB0.024%Llama 20.76382052 秒GPU1: 35 GB
GPU2: 33.9 GB0.12%
总结
本文我们用 LoRA 对三个大语言模型 (LLM) (RoBERTa、Mistral 7B 及 Llama 2) 针对灾难推文分类任务进行微调。从性能结果来看,RoBERTa 的性能大幅优于 Mistral 7B 和 Llama 2。这就提出了一个问题: 我们是否真的需要一个大而复杂的 LLM 来完成诸如短序列二分类这样的简单任务?
一个重要的启示是,在选择要使用的 LLM 模型时应该考虑具体的项目要求、可用资源和性能需求。
此外,对于针对短序列的相对 简单 的预测任务,小的基础模型 (例如 RoBERTa) 仍然具有竞争力。
最后,我们还通过例子展示了 LoRA 方法的通用性,其既可应用于编码器 (RoBERTa) 模型,还可应用于解码器 (Llama 2 及 Mistral 7B) 模型。
资源
- 本文代码均已在该 Github 项目。
- 下面是各模型的 Wandb 超参调优实验报告:
- RoBERTa
- Mistral 7B
- Llama 2
🤗 宝子们可以戳 阅读原文 查看文中所有的外部链接哟!
英文原文: https://hf.co/blog/Lora-for-sequence-classification-with-Roberta-Llama-Mistral
原文作者: Mehdi Iraqi
译者: Matrix Yao (姚伟峰),英特尔深度学习工程师,工作方向为 transformer-family 模型在各模态数据上的应用及大规模模型的训练推理。



 ufabet
มีเกมให้เลือกเล่นมากมาย: เกมเดิมพันหลากหลาย ครบทุกค่ายดัง
ufabet
มีเกมให้เลือกเล่นมากมาย: เกมเดิมพันหลากหลาย ครบทุกค่ายดัง


